standing test for mcl tear|mcl physical exam test : importers The medial collateral ligament, or MCL, of the knee can tear due to injury and cause pain. Treatment depends on the severity of the injury. Learn more about MCL tears here. Resultado da How much does @misticaoficial (Mística 🦋) earn on OnlyFans? 💸 misticaoficial, also known under the username @misticaoficial is a verified OnlyFans .
{plog:ftitle_list}
Resultado da Perfis. Serviços. Packs. Gabriel Derek Galvão. Não encontrou o que procurava?Para explorar os produtos e serviços de nossa comunidade.
valgus stress test positive result
tear film test slideshare
MCL Tear Grading. If you have an MCL tear, your health care professional will rate how serious your injury is by using one of these three grades: Grade 1 is a mild tear.A medial collateral ligament (MCL) injury is a stretch, partial tear, or complete tear of the ligament on the inside of the knee. A valgus trauma or external tibia rotation are the causes of this injury. Your therapist will gently press on the outside of your knee while it is slightly bent as well as when it is fully straight to test the strength of the ligament. The therapist will also check the inner side of your knee for . 13. Images. summary. A medial collateral ligament (MCL) knee injury is a traumatic knee injury that typically occurs as a result of a sudden valgus force to the lateral aspect of the knee. Diagnosis can be suspected with .
The medial collateral ligament, or MCL, of the knee can tear due to injury and cause pain. Treatment depends on the severity of the injury. Learn more about MCL tears here.
MCL Sprains and Tears: Causes and Risk Factors. Diagnosing MCL Sprains and Tears. Treatment Options and Recovery for MCL Sprains and Tears. A “popping” sound when the injury occurs. This sound is usually a sign of a grade II or .MCL injuries are often diagnosed from a physical exam alone, but your doctor may also complete the following tests to see how bad the sprain or tear is: X-rays, which can help rule out further . Grade 1: Mild pain and tenderness in the knee indicates an MCL sprain. Grade 2: Pain on the inside of the knee is more intense, and there might also be swelling. When the .In addition, your doctor may order the following tests: X-ray. This can show other damage and bone injury. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). This test is 90 percent accurate for .
ACL vs. MCL tears: Although symptoms of ACL and MCL tears are similar, a few key differences will help identify whether the injury affected the ACL or MCL. An ACL tear will have a more distinctive and loud popping sound than an MCL tear. The location of your pain and swelling could indicate either an ACL or MCL tear.
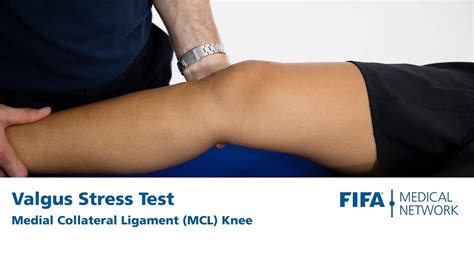
Rehabilitation after Injury to the Medial Collateral Ligament of the Knee Phase 1: The first six weeks after injury (grade 2 and 3) three weeks after injury (grade 1) The knee should be protected with a short-hinged brace for 3 to 6 weeks, depending upon the severity of the injury. Crutches and restricted weight bearing Medial collateral ligament assessment (valgus stress test) The medial collateral ligament (MCL) assessment involves the application of a valgus force to assess the integrity of the MCL of the knee joint. The instructions below are for examining the right knee, use the opposite hands if assessing the left knee. 1.Meniscus tears are the most common injury of the knee. Medial meniscus tears are generally seen more frequently than tears of the lateral meniscus, with a ratio of approximately 2:1. [2] Meniscal tears may occur in acute knee injuries in younger patients or as part of a degenerative process in older individuals.
special tests for mcl tear
Medial collateral ligament injuries of the knee: current treatment concepts. Curr Rev Musculoskelet Med. 2007;1(2):108-13., 2 Bollen S. Epidemiology of knee injuries: diagnosis and triage. Br J Sports Med. 2000;34(3):227-8. A person who experiences an MCL injury typically reports a combination of the following symptoms.An MCL tear can happen to anyone, but it is far more prominent with athletes. Learn more about MCL tears - symptoms, causes, and treatments. . They may also order some tests, such as an MRI or an X-ray scan, to help diagnose the tear. . Hao Z, Wen S. The effect of healing in the medial collateral ligament of human knee joint: A three . The MCL spans the distance from the end of the femur (thigh bone) to the top of the tibia (shin bone) and is on the inside of the knee joint.The MCL resists widening of the inside of the joint, which can be thought of as preventing "opening-up" of the knee. The medial collateral ligament (MCL) is an important structure that provides stability to the inside of your knee. Running from the thigh bone (the femur ) to the lower leg bone (the tibia ), this ligament prevents the knee from buckling inward into a .
An MCL tear is a painful but treatable condition, and most athletes return to their normal activities within a few weeks. Menu. Find a Doctor. Back. . Since MCL injury symptoms can be confused with symptoms of other medical conditions, your doctor may want to confirm an MCL tear with an X-ray, MRI or other test.
ACL and MCL tears can both cause pain, swelling, and instability. Learn the key differences between ACL vs MCL tears. . The medial collateral ligament (MCL) is a band of tissue located on the inner side of the knee joint. Like the ACL, it connects the femur to the tibia. . range of motion, and joint stability. Imaging tests such as MRI .The test is performed in conjunction with the Apley's distraction test. Meniscal injuries are very common and are associated with significant pain and morbidity. Meniscal injuries are less common in children younger than 10 years old. . (ACL) and the medial collateral ligament (MCL). When performing a physical examination, joint line .
Surgery for MCL Tears . MCL tears often do not need surgery. Many studies document successful nonsurgical treatment in nearly all types of MCL injuries. Most surgeons agree that for patients who complain of persistent knee instability, despite appropriate nonsurgical treatment, surgery is reasonable. Recovery time for MCL injuries will vary depending on severity of the MCL tear and if conservative treatment versus surgery is recommended. The healing time for a torn ligament that is treated without surgery may vary, again depending on the severity of the tear. Most MCL tears that are considered mild may take up to one month to heal. A . The medial collateral ligament, commonly referred to as the MCL, is a thick and strong ligament located along the inner side of the knee. The MCL stretches from the femur (thighbone) to the tibia (shinbone) and helps to stabilize the medial (inner) part of the knee. MCL Knee Injuries LCL Injury of the Knee . Meniscal tears are common sports-related injuries in young athletes and can also present as a degenerative condition in older patients. . standing at 20 degrees of knee .
Contact: An MCL injury usually occurs when there is a force through the outer side of a bent knee, e.g. a tackle hitting the outer side of the knee. This pushes the bones apart on the inside of the knee which overstretches the ligament . Valgus stress test (play video) The valgus stress test is a diagnostic test that is used in cases of suspected MCL injuries. The therapist takes hold of the leg, ensuring the knee is slightly bent (approx 30 degrees). .
The medial collateral ligament (MCL) is usually injured by pressure or stress on the outside part of the knee. A MCL injury can be a stretch, partial tear, or complete tear of the ligament. . The initial treatment for a medial collateral ligament (MCL) injury involves basic first aid. After swelling has gone down, though, it’s important to .I tore the ACL in half and partially tore the MCL. By the time the ACL was replaced, the MCL had gotten it's shit together. I can't speak to the pain level, but I know my biggest issue was the fear that it would happen again. I still have a tendency to stand up only on my good side unless I'm paying attention and trying to correct the bad habit.The knee joint allows the lower leg to flex (bend) or straighten (extend). To make certain that those are the only two motions that occur, four ligaments in the knee help control and protect it. The medial collateral ligament (MCL) is located on the medial aspect of the knee (medial = the closest to the center of the body) or inside of the knee.; The lateral collateral ligament (LCL) is . MCL sprains usually occur suddenly as acute knee injuries, however, they can develop gradually over time. Sudden onset/acute injuries. Medial collateral ligament injuries are common in contact sports such as football, rugby, and martial arts. However, they can also occur in daily activities such as falling and/or twisting action your knee joint.
What Are MCL Tears? An MCL tear is an injury to a ligament on the inside of the knee. MCL is an abbreviation for medial collateral ligament.The MCL is a strand of tough, fibrous tissue that connects the lower end of the thighbone or femur to the upper end of the shinbone or tibia.Its primary function is to stabilize the knee in standing and movement. An ACL injury is a tear or sprain of the anterior cruciate (KROO-she-ate) ligament (ACL) — one of the strong bands of tissue that help connect your thigh bone (femur) to your shinbone (tibia).ACL injuries most commonly occur during sports that involve sudden stops or changes in direction, jumping and landing — such as soccer, basketball, football and downhill . The medial collateral ligament (MCL) is a flat band of connective tissue that runs from the medial epicondyle of the femur to the medial condyle of the tibia. Its role is to provide valgus stability to the knee joint. MCL injuries often occur in sports, especially in skiing; in fact, 60% of skiing knee injuries involve the MCL. [1][2][3]Valgus Stress Test for Medial Collateral Ligament Injuries. . As a stand-alone test, it had a sensitivity of 78% and specificity of 67% the pain was used as the outcome measure and a sensitivity of 91% and specificity of 49% when laxity was the outcome measure. So, the absence of both pain and laxity seems to be of at least moderate clinical .
Patients with suspected meniscal tears experience medial or lateral joint-line discomfort and may have a sense of locking or catching. The Thessaly test is a dynamic reproduction of joint loading in the knee and the theory behind the test is that the knee with a meniscal tear will produce the same symptoms the patient reported.Medial collateral ligament (MCL) injuries are not super common in isolation; however, they do still occur mostly in sports and can be one of the structures involved in more serious knee injuries. . HOW: Begin by standing holding onto a medball. Step to the side with one leg landing quickly as you push the medball from your chest out to that .

Smartphone comparison. Find the best phones in terms of battery, camera, performance, and price in our comparison tool.
standing test for mcl tear|mcl physical exam test